appliedgenomics2023
Assignment 3: Mapping and WDLs
Assignment Date: Wednesday, September 20, 2023
Due Date: Wednesday, September 27, 2023 @ 11:59pm
Assignment Overview
In this assignment you will explore WDLs as a workflow language to orchestrate a variety of read mapping tasks. You can execute your WDLs using miniwdl after running pip install miniwdl. You may also find learn-wdl to be very helpful.
Miniwdl works best on Linux or older (non-M1) macs. If you are using a Mac, make sure to disable gRPC FUSE for file sharing. On M1 macs (and PCs) miniwdl wont run, but you can run miniwdl in the cloud via https://github.com/schatzlab-teaching/wdl101. Follow the instructions there to get started. Alternatively you can try to use the cromwell execution engine. Note you can install cromwell via mamba install cromwell.
The bioinformatics tools you will need for the assignment (bowtie, samtools, etc) are bundled into a Docker container so you wont need to install other software packages. This will get you ready to run your code in the cloud for future assignments. Instructions for running the container are available here: https://github.com/mschatz/wga-essentials. This is known to work on new macs (M1) and older macs (intel chip). It should also run on Linux and Windows but let us know if you have any issues.
As a reminder, any questions about the assignment should be posted to Piazza.
Question 1. de Bruijn Graph construction [10 pts]
- Q1a. Write a script to draw the de Bruijn graph for the following reads using k=3 (assume all reads are from the forward strand, no sequencing errors, complete coverage of the genome). You may find graphviz to be helpful (see below).
ATTCA
ATTGA
CATTG
CTTAT
GATTG
TATTT
TCATT
TCTTA
TGATT
TTATT
TTCAT
TTCTT
TTGAT
-
Q1b. Assume that the maximum number of occurrences of any 3-mer in the actual genome is 4 using the k-mers from Q1a. Write one possible genome sequence. Note this genome sequence may include sequences that are not supported by the underlying reads (this is the well known read decoherency problem for genome assembly).
-
Q1c. What would it take to fully resolve the genome? [In a few sentences]
Question 2. Hello World [5 pts]
- Using miniwdl, develop a Hello World workflow that takes in a user’s name (
USER_NAMEin string format) and outputs a file sayingHello, USER_NAME!. Please submit your code as well as a screenshot of the window in which you run the code. If you cannot successfully run miniwdl on your local computer or in the cloud, let us know as soon as possible so that we can provide an alternative.
Question 3. Mapping Analysis [10 pts]
The goal of this question is to develop a WDL that will align pairs of read file (paired or matepairs) and computes alignment statistics. Download the reads and reference genome (same as assignment 2) from: https://github.com/schatzlab/appliedgenomics2023/blob/main/assignments/assignment2/asm.tgz?raw=true
- Question 3a. Write a WDL that indexes the reference genome provided (
ref.fa):bowtie2-build GENOME.fa GENOME. Please submit your code as well as a screenshot of the window in which you run the code.
Note that the build comamnd outputs multiple files that you will need to mark as output files. You can either copy them one by one, or bundle them up in a tarball or zipfile.
- Question 3b. Write a WDL that aligns pairs of read files, sorts the alignments, and computes coverage statistics. Specifically it should run these steps
bowtie2 -x GENOME -1 PREFIX.1.fq -2 PREFIX.2.fq -S PREFIX.samsamtools sort PREFIX.sam -o PREFIX.bamsamtools stats PREFIX.bam > PREFIX.stats
Please submit the code for this but you do not need to include screenshots. Note that to run bowtie2, you will need all of the output files from the indexing step. You can either pass them in one by one, or you can bundle them all together as a tarball or zipfile as a “reference bundle”.
-
Question 3c. Using the WDL from b, plot the insert size distribution (tag: IS) and the coverage distribution (tag: COV) for the paired end reads (frag180.X.fq). Please include the code for plotting (this part does not need to be in the WDL)
-
Question 3d. Using the WDL from b, plot the insert size distribution (tag: IS) and the coverage distribution (tag: COV) for the mate pair reads (jump2k.X.fq). Please include the code for plotting (this part does not need to be in the WDL)
Question 4. Mappability Analysis [10 pts]
- 4a. Write a WDL to extract kmers of a specific length from a range of a given genome, and then align them back to a reference genome using bowtie2. Please submit the code for this but you do not need to include screenshots.
To extract the kmers, you will need to write your own script. You should label the kmer with the position in the genome so you can confirm it is mapped to the corrected position. For example, if the genome is:
>genome
GATTACA
It should output
>1
GAT
>2
ATT
>3
TTA
>4
TAC
>5
ACA
-
4b. Using your WDL with k = 25, extract every k-mer from positions 20,000,000 to 25,000,000 on GRCh38 chromosome 22, and align them back to chromosome 22 (the entire chromosome) using bowtie2. How many 25-mers are mapped back to the correct position (the place they were extracted from) with mapq >= 20? How many are mapped with mapq >= 20, but to an incorrect position? You can download chr22 from assignment 1 here: https://schatz-lab.org/appliedgenomics2023/assignments/assignment1/chr22.fa.gz
-
4c. We consider 25-mers that are mapped back to their correct position in the genome with mapq >= 20 to be uniquely mappable. For each position in 20,000,000-25,000,000 on chromosome 22, count how many uniquely mappable k-mers are mapped to it. Make a histogram of the number of positions in chromosome 22 with a given number of uniquely mappable k-mers overlapping them. Use k = 25, and the 25-mers you generated in part a. [Hint: How many 25-mers can uniquely map to any one base in chromosome 22?]
-
4d. Repeat the previous two questions for k = 50 and 100, and discuss (in a couple of sentences) the effect of k on how many k-mers are uniquely mappable and on how many uniquely mappable k-mers overlap each position in the genome.
Packaging
The solutions to the above questions should be submitted as a single PDF document that includes your name, email address, and all relevant figures (as needed). If you use ChatGPT for any of the code, also record the prompts used. Submit your solutions by uploading the PDF to GradeScope, and remember to select where in your submission each question/subquestion is. The Entry Code is: JK5VB4.
If you submit after this time, you will use your late days. Remember, you are only allowed 4 late days for the entire semester!
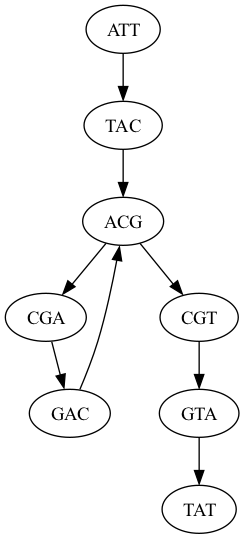
Graphview Tips
It is very easy to render a graph using graphviz. Install with mamba install graphviz. For example, these commands will render graph.dot using neato:
$ cat graph.dot
digraph{
ATT -> TAC
TAC -> ACG
ACG -> CGA
CGA -> GAC
GAC -> ACG
ACG -> CGT
CGT -> GTA
GTA -> TAT
}
$ neato -T png graph.dot -o neato.png
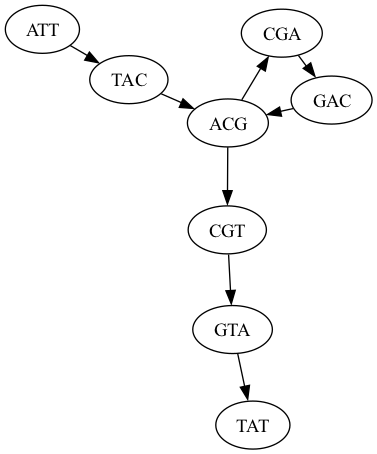
Alternatively use dot
$ dot -T png graph.dot -o dot.png